The IT operating model plays a crucial role in delivering business value to stakeholders. By organizing IT around composable capabilities and services that the entire organization can utilize, IT can advance to a new level. This shift transforms IT from a technology-driven, siloed function—typically managed as a cost center—into a business value enabler that collaborates closely with customer service, R&D, product development, logistics, manufacturing, and other essential business functions.
Service-oriented IT delivery is a strategic operating model in which IT capabilities are structured as modular, reusable services aligned with business outcomes. For large enterprises, this model is increasingly regarded as vital for achieving agility, scalability, and alignment with business needs amid digital transformation.
Many large enterprises are actively transitioning their IT toward service-oriented, “run IT like business” models. However, the adoption of these models is uneven. Some organizations are in the process of piloting service portfolios and capability-based architectures, while the most mature enterprises have successfully scaled service-oriented operating models and implemented business capability maps across their organizations.
Key findings
The adoption of “IT as‑a‑service” is strong. IT services are now seen as catalysts for innovation and growth; enterprises increasingly buy external services to accelerate AI, modernization and business outcomes — many expect service providers to guide strategy through execution. CIOs are urged to adopt a service‑optimizing IT operating model to “run IT like a business”. Enterprise Architecture maturity correlates with measurable outcomes: mature EA teams report better stakeholder engagement, visibility into redundant apps, and potential IT budget savings (estimates often in the ~11–30% range from de‑duplication and rationalization). However, culture, talent and legacy modernization as the main barriers to scale.
Here are the key findings of our brief research of current state of market adoption of modern IT as a Service models:
- Operating‑model redesign is widespread; two‑thirds of organizations have redesigned recently and many plan further change — redesigns aim to improve clarity, speed and value delivery, but success requires aligning structure, governance and talent.
- Redesign success depends on new rules: alignment among leaders, rewiring core processes, investing in people, and culture — not just org charts; using these rules improves odds of a successful service‑oriented shift.
- High‑performance IT organizations that are closer to service‑orientation deliver materially better business outcomes; structure and leadership are key differentiators.
- Business capability models are widely recommended but often under‑consumed; Gartner provides practical guidance to make capability models more intuitive, actionable and timely — capability modeling is a central artifact for service portfolios and roadmaps.
- EA and capability modeling is refered as a core to running IT as a service.
Current Stage of Adoption
Across Europe, the adoption of IT as a Service is accelerating, particularly in the areas of cloud-based solutions and platform-as-a-service models. Despite this momentum, maturity levels vary significantly across industries and countries. Many organizations continue to operate with IT-centric service models rather than fully transitioning to business-centric approaches, which limits the ability to align technology with strategic outcomes. Regulatory complexity and persistence of legacy infrastructure remain key barriers to transformation, slowing the pace of modernization. A notable case study from a German e-commerce company illustrates how leveraging ServiceNow in combination with Deloitte’s Service Management Enablement Framework enabled the organization to streamline employee onboarding, strengthen governance, and enhance operational efficiency—demonstrating the tangible benefits of structured IT service adoption.
In contrast, United States enterprises are further advanced in their journey toward service-oriented IT delivery. The widespread integration of enterprise service management (ESM) platforms has positioned US organizations at the forefront of maturity in this domain. Adoption is frequently supported by AI-driven tools and sophisticated automation frameworks, which enable scalable and resilient service delivery. According to McKinsey, 56% of large US organizations report on successful automation initiatives, underscoring the importance of strategic prioritization and human-centric design as critical success factors. This maturity reflects a broader cultural and operational shift toward embedding IT services as a core enabler of business transformation, rather than a supporting function.
These differences in maturity illustrate how strongly service-oriented IT shapes modernization outcomes across markets.
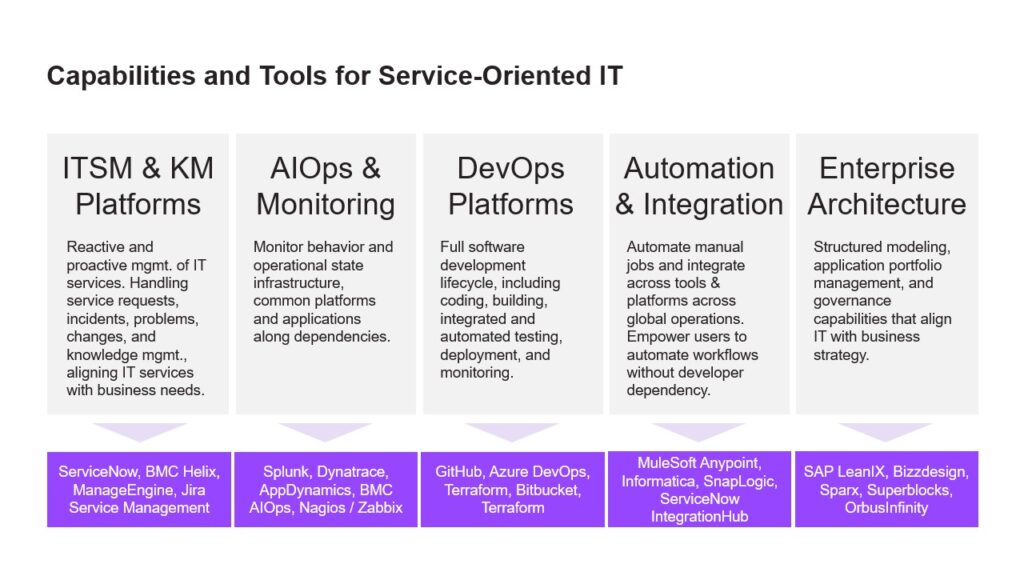
Key Tools and Platforms Enabling Service-Oriented Delivery
Successful service-oriented IT delivery depends not only on strategy and governance, but on the intelligent selection and orchestration of enabling platforms. Each category of tools plays a distinct role in shaping a resilient, scalable, and user-centric IT operating model. When aligned effectively, these platforms deliver tangible value across efficiency, agility, and experience.
ITSM Platforms such as ServiceNow, ManageEngine, HaloITSM, and InvGate form the backbone of reactive and proactive service management. They streamline incident, problem, change, and request workflows while embedding ITIL best practices into daily operations. These platforms are essential for maintaining service continuity and driving operational excellence.
AIOps and Monitoring Tools—including Splunk ITSI, Dynatrace, and New Relic—enable real-time visibility into infrastructure and application health. By leveraging machine learning and behavioral analytics, these platforms reduce alert noise, accelerate root cause analysis, and support predictive incident management.
Enterprise Service Management (ESM) platforms like Atomicwork and Freshservice extend ITSM principles across HR, finance, and facilities. They unify service delivery across departments, fostering a consistent user experience and enabling cross-functional automation.
Automation Frameworks—including CI/CD pipelines, API gateways, and service registries such as Netflix Eureka and Consul—support continuous delivery and integration. These tools empower DevOps teams to deploy faster, reduce manual effort, and maintain service reliability at scale.
Integration Platforms like MuleSoft, Boomi, and Azure Logic Apps ensure seamless data flow across disparate systems. They enable API-led connectivity, simplify orchestration, and support modular architecture—critical for agility in hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Finally, Knowledge Management Systems, increasingly powered by AI, play a pivotal role in enhancing service desk efficiency. These tools reduce handling time by 20–30% and improve first-contact resolution by 5–7%, directly impacting user satisfaction and operational throughput.
Together, these platforms form a cohesive digital ecosystem that enables service-oriented IT to thrive. By investing in the right mix of tools, enterprises can accelerate transformation, reduce costs, and deliver consistent, high-quality services across the organization.
Each of these platforms strengthens an organization’s ability to operate in a fully service-oriented IT model.
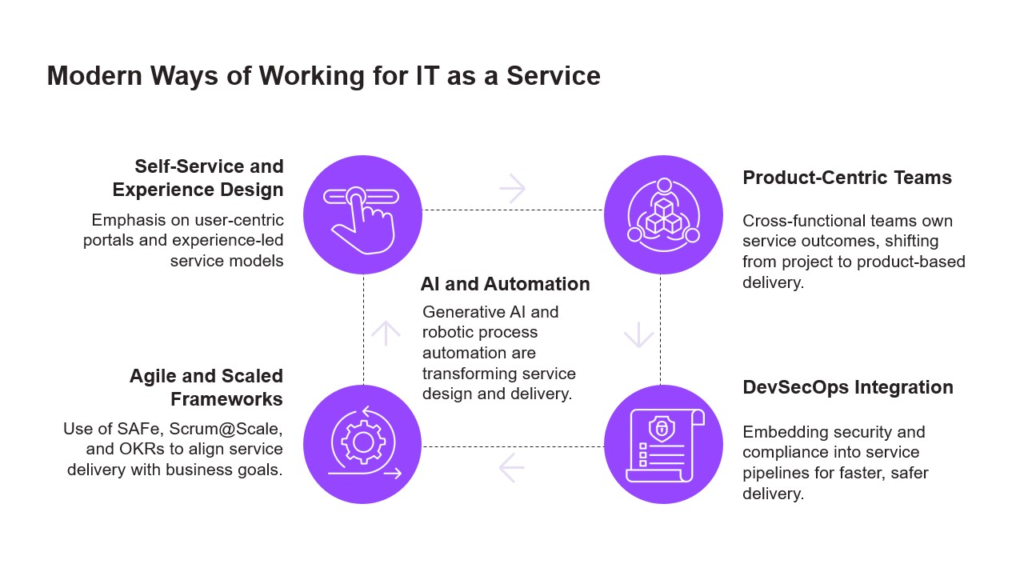
Modern Ways of Working for IT as a Service
The evolution of IT service delivery is being shaped by a convergence of agile methodologies, automation, and user-centric design. Enterprises are moving decisively toward modern ways of working, where speed, resilience, and experience are paramount.
At the core of this transformation is the shift to product-centric teams. Cross-functional units now own end-to-end service outcomes, replacing traditional project-based models with continuous delivery and accountability. This structure fosters agility, accelerates innovation, and aligns IT outputs with business value.
Security is no longer an afterthought. Through DevSecOps integration, organizations embed compliance and risk controls directly into service pipelines. This proactive approach enables faster, safer deployments and reduces friction between development and governance.
To scale effectively, enterprises are adopting Agile and Scaled Frameworks such as SAFe, Scrum@Scale, and OKRs. These frameworks provide the scaffolding to align IT delivery with strategic objectives, ensuring transparency, adaptability, and measurable progress across teams.
Meanwhile, AI and automation are redefining service design and execution. Generative AI and robotic process automation (RPA) are streamlining workflows, enhancing decision-making, and reducing manual effort. Already, 65% of organizations use automation for incident management, with another 20% planning adoption within the next year—underscoring its role as a strategic enabler.
Finally, the rise of self-service and experience design reflects a broader shift toward consumer-grade IT. With 88–90% of customers expecting online self-service portals, enterprises must prioritize intuitive, responsive interfaces that empower users and reduce support overhead.
Together, these pillars form a modern IT operating model—one that is agile, secure, automated, and experience-led. Modern delivery practices are essential enablers of a scalable service-oriented IT approach. Organizations that embrace these principles position themselves to deliver faster, smarter, and more resilient services in an increasingly digital world.
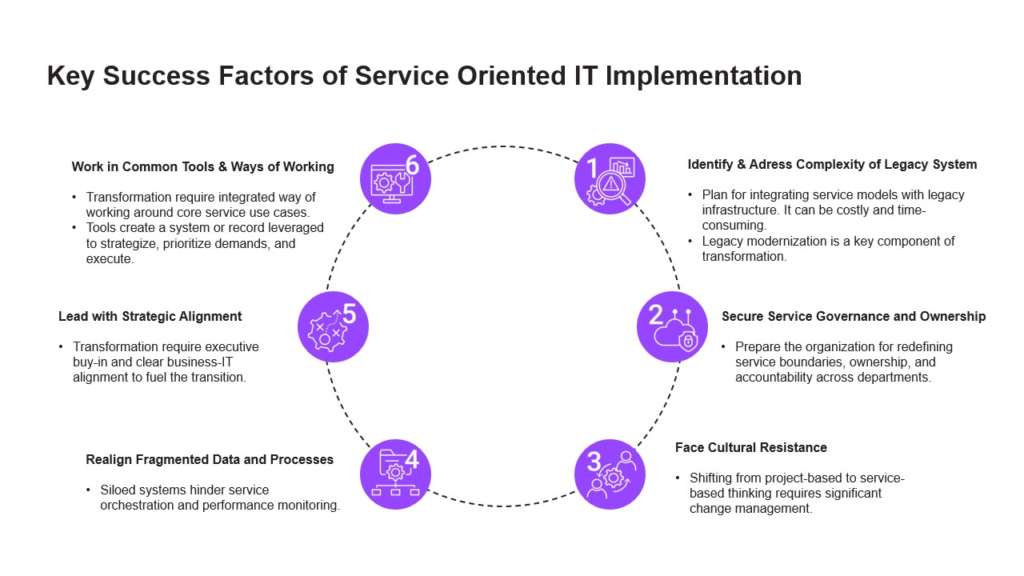
Key Success Factors for Implementing Service-Oriented IT
Transitioning to a service-oriented IT model is a strategic imperative—but success hinges on navigating several critical challenges. These factors must be addressed holistically to ensure sustainable transformation and measurable business impact.
Legacy System Complexity remains one of the most persistent barriers. Integrating modern service models with aging infrastructure is both costly and time-consuming. Enterprises must balance modernization with continuity, often requiring phased approaches and targeted investment in interoperability.
Service Governance and Ownership are equally vital. Redefining service boundaries, roles, and accountability across departments demands clear frameworks and executive sponsorship. Without structured governance, service sprawl and role ambiguity can undermine operational efficiency.
Cultural Resistance is a hidden but powerful obstacle. Shifting from project-based delivery to service-based thinking requires a fundamental mindset of change. Successful organizations invest in change management programs that build awareness, foster collaboration, and reinforce service ownership at all levels.
Fragmented Data and Processes pose a technical and organizational challenge. Siloed systems hinder orchestration, monitoring, and decision-making. A unified data strategy—supported by integration platforms and shared service models—is essential to unlock visibility and agility.
Finally, Leadership and Strategic Alignment is the cornerstone of transformation. Without executive buy-in and a clear business-IT alignment, initiatives stall or lose momentum. Leaders must articulate a compelling vision, align service outcomes with business goals, and empower teams to deliver autonomy and accountability.
Together, these success factors form the foundation for a resilient, scalable, and business-aligned IT operating model. Addressing them early and decisively enables organizations to accelerate transformation and realize the full value of service-oriented delivery.
Conclusions
Service-oriented IT delivery is no longer a future vision—it’s a strategic imperative. While adoption is progressing, especially in the US, EU enterprises must accelerate transformation to unlock full business value. Success depends on integrating modern tools, evolving ways of working, and overcoming deep-rooted organizational challenges. Real-world examples and data show that with the right strategy, governance, and technology, enterprises can scale service delivery and drive innovation across their operations.
References (14)
- How to create an effective operating model | McKinsey. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/people-and-organizational-performance/our-insights/a-new-operating-model-for-a-new-world
- What is an operating model and why does it matter? | McKinsey. https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/mckinsey-explainers/what-is-an-operating-model
- Getting your operation model redesign right | McKinsey. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/people-and-organizational-performance/our-insights/the-new-rules-for-getting-your-operating-model-redesign-right
- IT Services Are Catalysts For Innovation And Growth. https://www.delltechnologies.com/asset/en-us/services/support/industry-market/dellservices-forrester-spotlight-report.pdf.external
- The State Of High-Performance IT, 2024 | Forrester. https://www.forrester.com/report/the-state-of-high-performance-it-2024/RES181418
- Empowering the Digital Workplace with Enhanced Employee … – Zones. https://media.zones.com/images/pdf/forrester-report-the-state-of-the-service-desk-2024-report-pr.pdf
- Tool: Top Tips to Make Business Capability Models Successful – Gartner. https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/5679955
- Gartner Critical Capabilities for Enterprise Architecture Tools 2024 …. https://www.avolutionsoftware.com/news/gartner-critical-capabilities-enterprise-architecture-tools-2024/
- Gartner’s Enterprise Architecture Framework. https://enterprisearchitecture.work/docs/frameworks/130-gartner/gartners-enterprise-architecture-framework/
- The State of Enterprise Architecture 2024 – SITIC. https://sitic.org/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/State-of-Enterprise-Architecture-Report-2024.pdf
- As a service, at your service – Accenture. https://www.accenture.com/us-en/insights/high-tech/as-a-service-at-your-service
- Digital operating models | Deloitte Insights. https://www.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/topics/business-strategy-growth/digital-operating-models.html



